Tax Relief Measures Part of the Emergency Economic Measures in Response to COVID-19 in Japan~Exceptions for Tax Report for Election of Consumption Taxpayer・Stamp Tax Exemption for Special Loan Contracts・Special Measures for Fixed Asset Tax, etc.~
May 20, 2020
Introduction
On April 30, the Japanese government approved an emergency economic response plan to address the COVID-19 situation in Japan. Continuing from the previous article, we will look at the remaining tax relief measures.
Specific details regarding tax relief measures under the emergency economic measures as a response to COVID-19
Among the 12 tax measures under the emergency economic stimulus package for the new coronavirus infection, we will discuss the remaining six. In this issue, we are going to discuss the following:
⑥ Special provisions for submitting a tax report for the election of consumption taxpayers;
⑦ Exemption from stamp duty on contracts related to special loans;
⑧ Reduction of fixed assets tax and city planning tax on depreciable assets and business properties owned by small and medium-sized enterprises, etc.;
⑨ Expansion and extension of special treatment of property taxes to achieve a productivity revolution;
⑩ Extension of the temporary reduction of the environmental excise for motor vehicle tax and light motor vehicle tax;
⑪ Making the requirements for applying for the special measures of real estate acquisition tax for houses with seismic retrofitting more flexible; and
⑫ Other necessary measures.
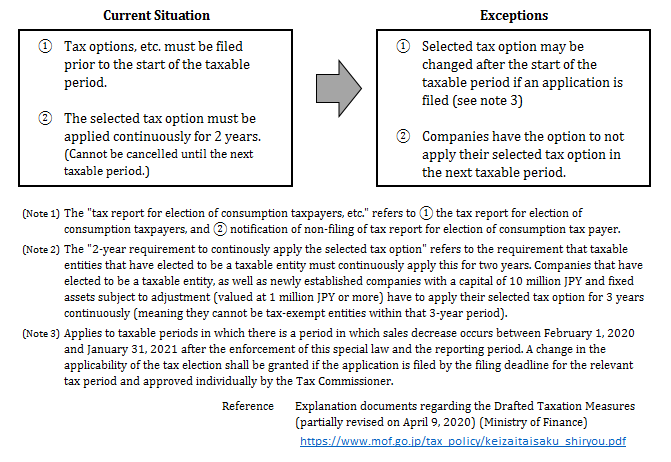
⑥ Special provisions for submitting a tax report for the election of consumption taxpayers
Businesses that experience a significant decrease in sales (approximately a decrease of 50% or more than sales figures in the same period from the previous year) during any given period (one month or more) between February 1, 2020, to January 31, 2021, due to the impact of COVID-19 will be allowed to change their consumption tax options after the start of the taxable period. In order to allow businesses to adapt to the actual situation of the business, the two-year continuity requirement on taxable entities is not imposed.
⑦ Exemption from stamp duty on contracts related to special loans
When both public and private financial institutions (*1) provide special loans under more favorable conditions to businesses affected by COVID-19, the stamp duty on the contract is exempted. In addition, this exemption is applied retroactively, so stamp tax is refunded even to those who have already signed contracts and paid their stamp tax.
*1 Public financial institutions: Japan Finance Corporation, Okinawa Development Finance Corporation
Private financial institutions: banks, credit unions, credit cooperatives, etc.
Others: Local governments, etc.
⑧ Reduction of fixed assets tax and city planning tax on depreciable assets and business properties owned by small and medium-sized enterprises, etc.
Depending on the amount of decrease in sales, the fixed assets tax and city planning tax for fiscal year 2021( *2) on depreciable assets and business properties owned by small and medium-sized businesses, etc., may be reduced to either half or even zero. Specifically, the tax rate will be halved if sales for any three-month period between February and October 2020 decreased by 30% to less than 50% compared to the same period in the previous year, and if sales decrease by 50% or more, the tax will be waived.
*2 For fiscal year 2020, fixed assets tax and city planning tax can be postponed for one year if income decreases by 20% or more compared to income during the same month in the previous year, thanks to the “special exception to the tax payment deferral system” we have discussed previously.
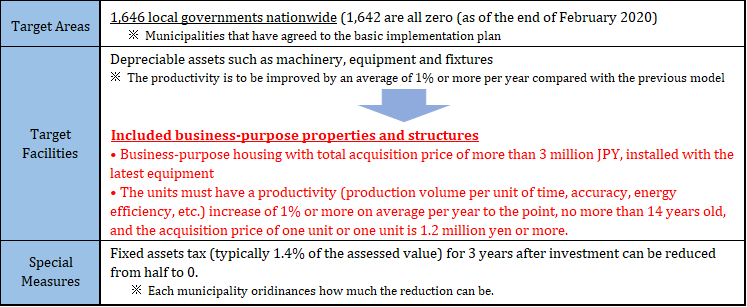
⑨ Expansion and extension of special treatment of property taxes to achieve a productivity revolution
Currently, there are special measures in place that can exempt or reduce property taxes on certain newly invested equipment by small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) for three years after the investment, following local government ordinances. From the perspective of supporting SMEs that invested in new equipment despite the effects of COVID-19, business properties and structures will be added to the list of applicable items in addition to depreciable assets such as machinery, equipment, and fixtures; moreover, the deadline for application will be extended for two years from the end of March 2021 to the end of March 2023, on the assumption that the Act on Special Measures for Productivity Improvement will be revised.
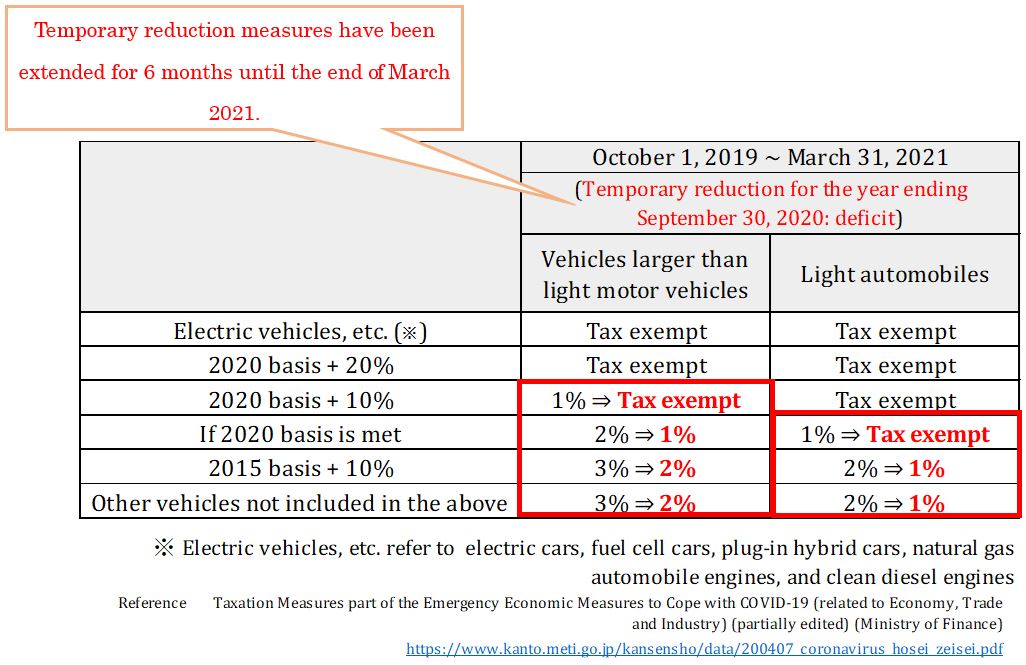
⑩ Extension of the temporary reduction of the environmental excise for motor vehicle tax and light motor vehicle tax
As a temporary special measure in response to the increase in the consumption tax rate, the deadline for the application to reduce the 1% motor vehicle tax and light motor vehicle tax rate environmental performance rate for private vehicles and light vehicles (including used ones) purchased between October 2019 and the end of September 2020 has been extended by six months, and will apply to vehicles acquired by the end of March 2021.
⑪ Making the requirements for applying for the special measures of real estate acquisition tax for houses with seismic retrofitting more flexible
Special measures for real estate acquisition tax( *3) in the case of seismic retrofitting of an existing structure that does not conform to seismic standards may be applied even if the tenant fails to move in within six months of acquisition if certain conditions are met (until the end of fiscal year 2021).
*3 Under the current system, if the existing structure that does not conform to the earthquake resistance standards is within six months from the date of acquisition, a certain amount of deduction will be made from the tax base amount of real estate acquisition tax (the price of the house) depending on when the time reconstruction is done, as long as the following conditions are met:
1) Seismic retrofitting will be done;
2) The structure will receive a certificate of compliance with earthquake resistance standards; and
3) It will be occupied.

⑫ Other necessary measures
Subsidies for struggling households and temporary special benefits for households with children, which will be implemented under the “Emergency Economic Measures to Cope with COVID-19”, will be exempted from income tax and individual inhabitant tax.
Conclusion
Following the previous column, we have explained the tax measures under the Emergency Economic Measures to Cope with COVID-19 per item. Although these tax measures are only meant to provide financial support, there is no reason not to take advantage of what is available.
The impact of COVID-19 on society and the economy has been enormous. As part of its emergency economic stimulus package, the government has pledged to implement economic stimulus measures of a drastic scale without being limited by precedents, and by mobilizing all policy measures, including fiscal, monetary, and tax measures, and to continue to take timely action as needed, taking into account the needs of all individuals.
With COVID-19 possibly considered as Japan’s biggest crisis since the war and with no way to predict how the situation will develop, everyone turns to checking information that is updated daily. With all the information available, please take the time to review the information you find necessary, as well as continue to pay attention to the daily changes in the situation and present information.